现代C++实现多种print
现代C++实现多种print
目录
学习C++的朋友会遇到这样的问题,有char,int,double等对象,我们想把它们打印出来看看,初学者会通过cout或者传统C语言的printf函数来打印这些对象。
例如:
int i = 1;
char c = 'f';
double d = 3.14;
//cout
cout << i << endl;
cout << c << endl;
cout << d << endl;
//printf
printf("%d\n%c\n%f", i, c, d);
传统C中的printf 函数,虽然也能达成不定个数的形参的调用,但其并非类别安全,写输出格式也不方便,而且支持的是基础类型。使用cout缺点在于代码量会比较多,不好看。所以,能不能很简单地打印出每一个元素呢?
Print Version1#
幸运的是,有更好的解决方案,那就是使用C++11引入的variadic template,先来看看第一个版本的print,并介绍variadic template,代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
// version1
void print1() {};
template <typename T, typename... Types>
void print1(const T& firstArg, const Types&... args)
{
cout << firstArg << endl;
print1(args...);
}
int main()
{
print1(7.5, "hello", bitset<16>(377), 42);
return 0;
}
Variadic Template: 是指数量不定,类型不定的模板,如上所示的print函数,可以看到接受了不同类型的参数,调用的函数就是拥有Variadic Template的函数,print(7.5, "hello", bitset<16>(377), 42)运行的时候,首先会7.5作为firstArg,剩余部分就是一包,然后在函数内部,继续递归调用print函数,然后把"hello"作为firstArg, 其余的作为一包,一直递归直到一包中没有数据,调用边界条件的print(空函数)结束。
函数的...表示一个包,可以看到,用在三个地方,
-
第一个地方是模板参数
typename...,这代表模板参数包。 -
第二个就是函数参数类型包(
Type&...), 指代函数参数类型包。 -
第三个就是函数参数包
args...,指的是函数参数包。另外,还可以使用
sizeof...(args)得到包的长度。
总的来说,上面是一种递归解决方案,依次展开参数包,然后进行操作。
Print Version2#
你可能觉得上述边界条件的print函数有些多余,比version1更简洁的就是下面的version2:
template < typename T , typename ... Types>
void print2 (const T& firstArg , const Types&... args)
{
cout << firstArg << endl;
if constexpr ( sizeof ...(args) > 0) print2 (args...) ;
}
上述函数能够实现version1一样的功能,通过判断args的长度来选择是否结束递归,constexpr可以确保在编译期间去创建空的print边界条件以及print函数。
Print Version3#
除了递归,还有一种通过逗号表达式和初始化列表的方式来解开参数包。
template < typename T , typename ... Types>
void print3 (const T& firstArg , const Types&... args)
{
cout << firstArg << endl ;
initializer_list <T> { ( [&args] {cout << args << endl;}(), firstArg )...};
}
其中的[&args] {cout << args << endl;}()是构建了一个lambda表达式,并直接运行,没有]和{之间省略了(),所谓逗号表达式展开是指initializer_list会将( [&args] {cout << args << endl;}(), firstArg )...展开为([&args1] {cout << args1 << endl;}(), firstArg),…. ,([&argsN] {cout << argsN << endl;}(), firstArg),内部的lambda表达式只会生成临时对象,所以最后的initializer_list变为了N个firstArg,也就是类型为T,所以initializer_list后面才会接上<T>。当然也可以将initializer_list打印出来看看:
template < typename T , typename ... Types>
void prin3_test (const T& firstArg , const Types&... args)
{
cout << firstArg << endl ;
auto i_l = initializer_list <T> { ( [&args] {cout << args << endl;}(), firstArg )...};
for (auto i : i_l)
cout << i << endl;
}
另外, 逗号表达式可以接上多个,不限于一个:
initializer_list <T> {
( [&args] {cout << args << endl;}(), [&args] {cout << args << endl;}(), firstArg)...};
Print Version4#
知道上面的initializer_list的解包方式, 还可以只使用一行实现print:
template <typename ... Types>
void print4 (const Types&... args)
{
initializer_list <int> { ([&args] {cout << args << endl;}(), 0)...};
}
关键在于直接传递参数包 , 第一个参数不需要分开 , 如此就可以达到一行实现print的功能.
容器的Print#
上述的print只能针对那些基础类型以及重构了<<操作符的自定义对象, 对于STL中的容器, 则需要自己重载操作符, 下面给出vector的重载操作符函数(当然容器内部的对象也需要重载<<):
template <typename T>
ostream& operator << (ostream& os, const vector<T>& vec){
os << "{ ";
for (auto& v : vec)
os << v << ' ';
os << "}";
return os;
}
重载后, 也可以使用上述的print函数了, 除了tuple容器以外, 其他容器的重载操作符与上述类似, 有些许差异.
tuple容器的print#
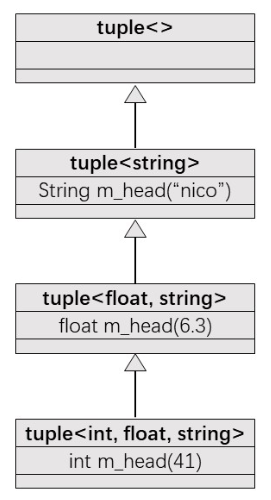
tuple是C++11提出来的, 内部实现使用的是variadic template, 所以需要特别处理. 下面给出tuple一种基于递归继承的简洁实现:
template <typename ... Values> class mytuple1; //前向申明
template <> class mytuple1<> {}; //递归终止类
template <typename Head, typename ... Tail>
class mytuple<Head, Tail...> : private mytuple1<Tail ...> //递归继承
{
using inherited = mytuple1<Tail...>;
public:
mytuple1() {}
mytuple1(Head v, Tail... vtail) : m_head(v), inherited(vtail...) {}
Head head() {return m_head;}
inherited& tail() {return *this;}
protected:
Head m_head;
};
mytuple1<int, float, string> t(41, 6.3, "nico");
print1(t1.head(), t1.tail().head(), t1.tail().tail().head());
上述继承关系可以表示为如下结构:
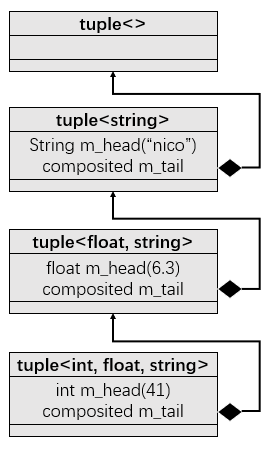
tuple还有一种递归组合的实现方式, 也列出来, 有兴趣的朋友也可以看看:
template <typename ... Values> class mytuple2;
template <> class mytuple2<> {};
template <typename Head, typename ... Tail>
class mytuple2<Head, Tail...>
{
using composited = mytuple2<Tail...>;
public:
mytuple2() {}
mytuple2(Head v, Tail... vtail) : m_head(v), m_tail(vtail...) {}
Head head() {return m_head;}
composited& tail() {return m_tail;}
protected:
Head m_head;
composited m_tail;
};
结构图就不是继承了,而是组合了,与上面类似:
现在来重载tuple容器的操作符, 代码如下:
template <int IDX, int MAX, typename... Args>
struct PRINT_TUPLE {
static void print (ostream& os, const tuple<Args...>& t){
os << get<IDX>(t) << (IDX + 1 == MAX ? "": ",");
PRINT_TUPLE<IDX+1, MAX, Args...>::print(os, t);
}
};
template <int MAX, typename... Args>
struct PRINT_TUPLE<MAX, MAX, Args...> {
static void print (ostream& os, const tuple<Args...>& t){
}
};
template <typename ... Args>
ostream& operator << (ostream& os, const tuple<Args...>& t) {
os << "[";
PRINT_TUPLE<0, sizeof...(Args), Args...>::print(os, t);
return os << "]";
}
一个技巧是通过sizeof...求出参数包的长度, 然后从建立一个索引, 依次调用get函数打印元素, 直到索引等于包的长度调用递归结束函数, 其中PRINT_TUPLE类中的是否打印逗号也是一样的道理.
结语#
最后附上所有代码, 以供试玩, 建议在C++17环境运行, if constexpr是C++17引入的新功能.
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <tuple>
using namespace std;
// version1
void print1() {};
template <typename T, typename... Types>
void print1(const T& firstArg, const Types&... args)
{
cout << firstArg << endl;
print1(args...);
}
// version2
template < typename T , typename ... Types>
void print2 (const T& firstArg , const Types&... args)
{
cout << firstArg << endl;
if constexpr ( sizeof ...(args) > 0) print2 (args...) ;
}
// version3
template < typename T , typename ... Types>
void print3 (const T& firstArg , const Types&... args)
{
cout << firstArg << endl ;
initializer_list <T> {
( [&args] {cout << args << endl;}(), firstArg)...};
}
// version4
template <typename ... Types>
void print4 (const Types&... args)
{
initializer_list <int> { ([&args] {cout << args << endl;}(), 0)...};
}
template < typename T , typename ... Types>
void print3_test1 (const T& firstArg , const Types&... args)
{
cout << firstArg << endl ;
auto i_l = initializer_list <T> {
( [&args] {cout << args << endl;}(), firstArg)...};
for (auto i : i_l)
cout << i << endl;
}
template < typename T , typename ... Types>
void print3_test2 (const T& firstArg , const Types&... args)
{
cout << firstArg << endl ;
auto i_l = initializer_list <T> {
( [&args] {cout << args << endl;}(), [&args] {cout << args << endl;}(), firstArg)...};
for (auto i : i_l)
cout << i << endl;
}
template <typename T>
ostream& operator << (ostream& os, const vector<T>& vec){
os << "{ ";
for (auto& v : vec)
os << v << ' ';
os << "}";
return os;
}
template <typename ... Values> class mytuple1;
template <> class mytuple1<> {};
template <typename Head, typename ... Tail>
class mytuple1<Head, Tail...> : private mytuple1<Tail ...>
{
using inherited = mytuple1<Tail...>;
public:
mytuple1() {}
mytuple1(Head v, Tail... vtail) : m_head(v), inherited(vtail...) {}
Head head() {return m_head;}
inherited& tail() {return *this;}
protected:
Head m_head;
};
template <typename ... Values> class mytuple2;
template <> class mytuple2<> {};
template <typename Head, typename ... Tail>
class mytuple2<Head, Tail...>
{
using composited = mytuple2<Tail...>;
public:
mytuple2() {}
mytuple2(Head v, Tail... vtail) : m_head(v), m_tail(vtail...) {}
Head head() {return m_head;}
composited& tail() {return m_tail;}
protected:
Head m_head;
composited m_tail;
};
template <int IDX, int MAX, typename... Args>
struct PRINT_TUPLE {
static void print (ostream& os, const tuple<Args...>& t){
os << get<IDX>(t) << (IDX + 1 == MAX ? "": ",");
PRINT_TUPLE<IDX+1, MAX, Args...>::print(os, t);
}
};
template <int MAX, typename... Args>
struct PRINT_TUPLE<MAX, MAX, Args...> {
static void print (ostream& os, const tuple<Args...>& t){
}
};
template <typename ... Args>
ostream& operator << (ostream& os, const tuple<Args...>& t) {
os << "[";
PRINT_TUPLE<0, sizeof...(Args), Args...>::print(os, t);
return os << "]";
}
int main()
{
print1(7.5, "hello", bitset<16>(377), 42);
print2(7.5, "hello", bitset<16>(377), 42);
print3(7.5, "hello", bitset<16>(377), 42);
print4(7.5, "hello", bitset<16>(377), 42);
print1(vector<int> {1, 2, 3, 4});
print2(vector<int> {1, 2, 3, 4});
print3(vector<int> {1, 2, 3, 4});
print4(vector<int> {1, 2, 3, 4});
mytuple1<int, float, string> t1(41, 6.3, "nico");
print1(t1.head(), t1.tail().head(), t1.tail().tail().head());
mytuple2<int, float, string> t2(41, 6.3, "nico");
print1(t2.head(), t2.tail().head(), t2.tail().tail().head());
cout << make_tuple(41, 6.3, "nico");
return 0;
}